
When you think of business growth, the first thing that comes to mind tends to be customer acquisition. But there is another important metric that is often overlooked – Customer Lifetime Value, or CLV.
Before looking for new customers, you should make sure you’re making the most of your existing customer base.
One of the most overlooked avenues to business growth can be increasing customer lifetime value. Moreover, tracking this metric is a vital financial KPI for monitoring overall business health. It can help businesses discover key obstacles to their success like churn rate, abandoned carts, missed upselling opportunities, and customers going cold on you.
In this blog, we’ll explain all you need to know about what customer value is, how to track it, and key strategies for improving it.
What is Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)?
Customer Lifetime Value reveals how much revenue a business can expect from a customer across the entirety of your relationship with them. It takes into account not only the initial purchase and how much it cost to bring on the customer, but also the frequency of purchases, the average order value, the duration of the customer relationship, and the potential for referrals, upsells, or repeat business.
CLV is calculated by multiplying the Average Purchase Value (APV), the Average Purchase Frequency Rate (APFR), and the Average Customer Lifespan (ACL). This calculation provides an estimate of the total revenue a business can expect from a customer throughout their relationship.
Why is CLV Important?
Calculating CLV helps businesses understand the long-term value of acquiring and retaining customers, guiding strategic decisions in marketing, sales, and customer service.
Businesses can identify high-value customers and allocate resources more effectively to better nurture these relationships. Moreover, businesses can use CLV analysis to optimize their marketing strategies and tailor efforts towards acquiring customers with the highest potential long-term returns.
A proper understanding of CLV reveals key insights into a business’s operational health and empowers businesses to make informed decisions. There are countless benefits to tracking CLV, but there are a few reasons it’s critically important too.
These are the main areas of business tracking CLV effects:
- Resource Allocation. CLV is crucial for current and future decision-making. It enables businesses to analyze better for sales, pricing, and advertising to improve ROI on the fly. It also improves forecasting accuracy, allowing for informed decision-making regarding inventory, production, and other costs to avoid overspending.
- Driving Repeat Sales. Measuring CLV involves tracking the average number of sales from loyal customers and identifying key factors that drive customer engagement through surveys. This empowers businesses to choose the right strategies and types of sales methodology to encourage repeat purchases.
- Customer Acquisition. CLV considers the long-term value of a customer, guiding decisions on how much to invest in acquiring new customers compared to their potential lifetime value.
- Customer Segmentation. By calculating CLV, businesses can identify high-value customers and tailor marketing efforts for more effective campaigns, fostering meaningful engagement and personalized experiences.
- Long-term Growth. CLV emphasizes the importance of customer experience and retention, serving as a foundation for strategies to retain customers, increase revenue from less valuable customers, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
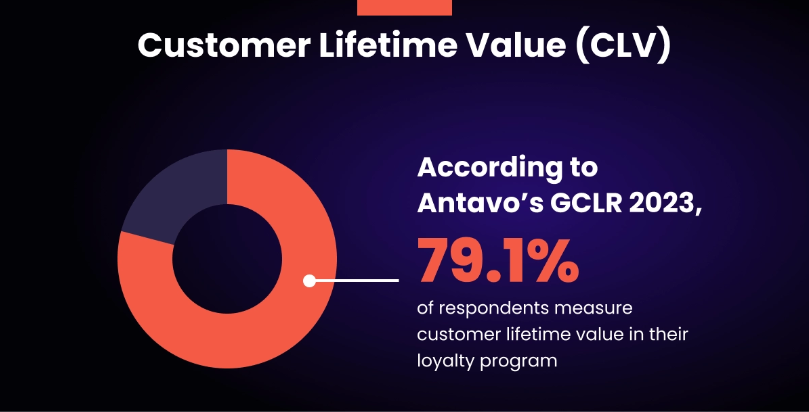
A Step-By-Step Guide to Calculating CLV
Calculating CLV is crucial for businesses aiming to understand their customers’ long-term worth. This guide provides the key KPIs you’ll need to calculate your CLV, and the key metrics you should evaluate in tandem with it.
Our pro tip: Using digital tools and technologies to automate the entire financial planning system is one of the best ways to maximize revenue.
1. Gather Data
To calculate CLV, you’ll need to start by gathering comprehensive data sets of customer transactions, such as purchase history, average order value, and the duration of customer relationships. This data should all be readily available on your CRM or CX platform.
It’s imperative to ensure the accuracy and completeness of records detailing revenue generated from each customer. Here are the key figures you’ll need to collect:
- Average Purchase Value (APV) – Aggregate the total revenue generated from all customer transactions, then divide this figure by the total number of transactions. This computation yields the APV, a fundamental metric in assessing customer spending habits.
- Average Purchase Frequency Rate (APFR) – Quantify the total number of purchases made across all customers during a specified time frame. Subsequently, ascertain the total count of unique customers who engaged in transactions during the same period. Divide the total number of purchases by the total number of unique customers to derive the APFT, a critical indicator of customer engagement.
- Average Customer Lifespan (ACL) – Evaluate the average duration of customer relationships, a metric influenced by diverse factors such as business model and customer behavior. Utilize historical data or industry benchmarks to compute the ACL, a pivotal element in forecasting long-term customer value.
2. Calculate CLV
Then, as we outlined earlier, you just need to multiply these integers together:
APV x APFR x ACL = CLV.
Simple!

3. CLV-to-Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
Once you have your CLV there’s one other metric you’ll want to compare it with to really gain the key insights it can offer: The Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
If you have a CLV-to-CAC ratio exceeding one, your business generates more revenue from each customer than the cost of acquiring them.
The CAC is the total average amount of money spent by a business in the acquisition of a new customer. It should include all expenses from marketing to sales efforts, and other resources directed towards attracting new customers.
To calculate your CAC, sum up all expenses associated with customer acquisition costs over a defined period. Divide the total acquisition costs by the number of new customers acquired within that timeframe to ascertain the Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), a critical parameter in evaluating the efficiency of acquisition strategies.
For example, a software company spent $20,000 on advertising in September, $25,000 on salaries for sales and marketing , and $5,000 on tools relating to advertising. For the month of September, they got 100 new customers. Therefore their CAC would be $50,000/ 100 which equals $500, which is the amount they spent to acquire each new customer that month. CAC can also be calculated per quarter or year or any other time period that is decided on.
4. Analyze and Iterate
Next, you’ll need to establish a cyclical process of revisiting and updating CLV calculations in response to evolving customer behavior and market dynamics.
You might opt to automate this process using digital tools and AI, alternatively, you can incorporate a regular check on your CLV as part of your operational audit.
How to Use CLV to Grow Revenue
Now that you’re ready with your CLV and regular monitoring process, you need to know how to use it. There are a number of valuable practices to incorporate CLV analysis into in order to divine fantastic insights into the operational health and growth opportunities for your business.
High-value Customers
Leveraging CLV insights helps businesses identify the customers most likely to yield significant long-term revenue. This means you can tailor acquisition strategies towards attracting and retaining these high value customers effectively.
By focusing resources on acquiring customers with the highest potential lifetime value, businesses can optimize marketing ROI and drive sustainable growth. Top tip for marketers: CLV stats can be hugely persuasive in ‘winning’ budget for your department.
Brand Advocacy
CLV analysis can also help to identify brand advocates too. Businesses that cultivate these relationships can foster positive word-of-mouth referrals. Having brand advocates in your customer base, and encouraging that advocacy, is a fantastic way to drive sustained revenue growth and brand reputation.
Value-tier Customer Segmentation
Monitoring CLV lets businesses segment their customer base and tailor marketing efforts and customer experiences according to each segment’s value potential. This means businesses can allocate resources to the segments that offer the highest ROI.
Moreover, understanding the distinct needs and behaviors of different customer segments, businesses can deploy targeted strategies to increase the CLV of underperforming segments.
Customer Retention
The most immediate benefit to monitoring CLV is identity crisis areas for customer retention. By monitoring CLV trends and behavioral indicators, businesses can proactively identify customers at risk of churn.
By detecting early signs of disengagement or dissatisfaction, businesses can implement targeted retention strategies to strengthen customer relationships and preserve revenue streams.
Operational Weak Points
Conducting in-depth analysis of CLV data helps to pinpoint areas of underperformance in the customer lifecycle journey. By identifying weak points such as low retention rates or suboptimal conversion rates, businesses can implement strategies to improve customer satisfaction, loyalty, and overall profitability.
Yearly Advertising Budget
CLV analysis can also provide fantastic insights for building your budget too. By allocating resources based on the expected lifetime value of different customer segments, businesses can prioritize investments in acquisition and retention efforts that yield the highest returns. This ensures efficient use of marketing resources and maximizing overall profitability.
Ad Performance
Optimizing the effectiveness of advertising campaigns can also be affected by tracking their impact on CLV metrics. It provides businesses with the insights they need to optimize campaign performance and enhance return on investment.
By analyzing how advertising initiatives influence customer acquisition, retention, and overall lifetime value, businesses can refine their marketing strategies. They may find that their digital marketing campaigns outperform their physical, vice versa, or suggest that they should explore the intersection between the two: phygital marketing.
Keep Your Customers Coming Back Again and Again
Tracking CLV is not just beneficial—it’s essential for maximizing ROI, refining customer acquisition strategies, and nurturing lasting customer relationships.
In the quest for business growth, focusing solely on customer acquisition can mean missing out on the potential within the existing customer base. By understanding the components of CLV and leveraging it to inform decisions across marketing, sales, and customer service, businesses can optimize resource allocation, drive repeat sales, and foster long-term growth.
Did you learn a lot about CLV in this article?
Here are three more to read next: